At the recently concluded NVIDIA GTC conference in Washington, Jen-hsunHuang repeatedly emphasized that “researchers need open – source. Developers rely on open – source. Companies around the world, including us, cannot do without open – source models. Open – source is extremely, extremely important.” Under Jen-hsunHuang’s call, a heavyweight new player has entered the field of omni – modal understanding models. NVIDIA has open – sourced OmniVinci, an omni – modal large language model (Omni – Modal LLM) capable of understanding the multi – modal world. This model achieves unified understanding of vision, audio, and language in the same latent space, enabling AI to not only recognize images and understand speech but also reason, converse, and generate content. This 9B visual – speech understanding omni – modal model has become an instant hit since its launch. In just one week, the model weights on Huggingface have been downloaded over 10,000 times!
Outperforming Competitors in Multi – Modal Understanding Performance
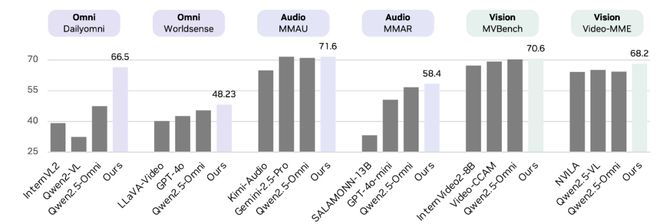
Compared with similar – sized omni – modal model competitors, OmniVinci has achieved significant advantages in multiple commonly used multi – modal benchmark tests. These include a +19.05 improvement in the video – audio cross – modal understanding task (DailyOmni), a +1.7 improvement in audio understanding (MMAR), and a +3.9 improvement in video understanding (Video – MME), demonstrating its excellent omni – modal understanding capabilities. More importantly, OmniVinci has achieved this outperformed with nearly six times less data, showcasing the remarkable efficiency of its architecture and data engine.
Three Architectural Innovations: Enabling Visual and Auditory Senses to Resonate in the Same Space
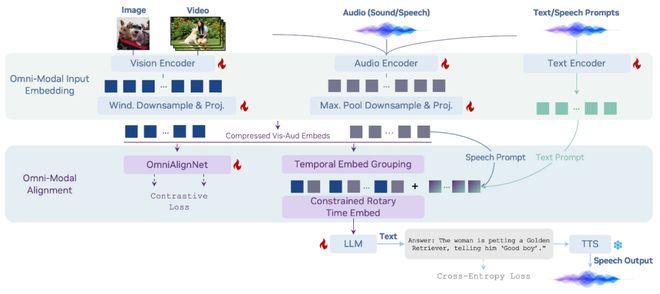
OmniVinci not only boasts impressive benchmark performance but also, through extensive scientific experiments in its paper, explores the optimal architecture for omni – modal models rather than simply stacking training data, a practice that is clearly more worthy of reference. Imagine that when an AI watches a video, the visuals (vision) and audio (audio) are two separate streams of information. If the model architecture doesn’t handle this well, the AI will be “schizophrenic.” OmniVinci aims to make them perfectly synchronized, achieving this through three core innovative designs:
OmniAlignNet: Cross – Modal Semantic Alignment Network
This is like a “super translator” that enables the model to “see sounds and understand visuals” in the same space. It creates a shared space and, through contrastive learning, allows visual and audio signals to communicate without barriers using the same “language,” achieving in – depth cross – modal alignment.
Temporal Embedding Grouping (TEG): Temporal Embedding Grouping Mechanism
It reorganizes visual frames and audio signals according to timestamps, enabling the model to perceive the relative temporal order of events across modalities. The AI can finally figure out whether it’s “shooting first and then hearing the gunshot” or “lightning first and then thunder.” By grouping according to timestamps, the AI understands the sequence of events.
Constrained Rotary Time Embedding (CRTE): Constrained Rotary Time Embedding
Through time – rotary encoding, the model gains absolute time perception capabilities. The AI not only knows “before” and “after” but also knows whether an event occurs at the 5th second or the 50th second of a video.
With these three “tricks,” OmniVinci truly possesses the ability to accurately perceive vision, audio, and the passage of time.
Data Engine: Behind 24M Multi – Modal Dialogues
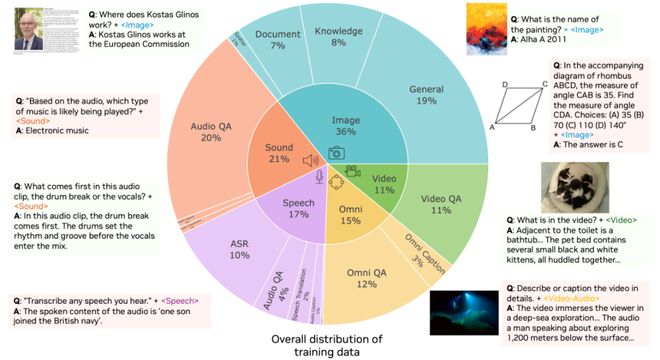
Model strength is inseparable from data support. The OmniVinci team has built a massive omni – modal data engine (Omni – Modal Data Engine), covering a total of 24 million multi – modal dialogue samples across the four domains of images, videos, audio, and speech. In terms of data distribution, images account for 36%, audio and speech together account for 38%, videos account for 11%, and omni – modal data accounts for 15%. It includes two innovative omni – modal learning methods:
Implicit Learning
It directly utilizes existing video – audio question – answering data, allowing the model to “listen to sounds” while “watching videos.”
Explicit Learning
AI separately generates descriptions specific to the visual and audio modalities and then has the LLM perform cross – correction and fusion, solving the “hallucination” problem (such as misjudging semantics by just looking at the picture) common in single – modal models.
Experiments: Key Insights into Building Omni – Modal Models
[Key Insight 1] Single – Modal Labeling = Unreliable! Say Goodbye to “Modal Hallucinations”
The team found that many AI models suffer from “modal hallucinations.” When only looking at the picture (vision), an AI might see a deep – sea robot and “imagine” that it represents the victory of human high – technology. When only listening to the voice – over (audio) saying “the deepest part of the Earth,” the AI might “guess” that it’s a documentary about the Earth’s core. Therefore, a joint captioning method that integrates both modalities is crucial for comprehensive understanding.
[Key Insight 2] 1 + 1 > 2! When Hearing “Illuminates” Vision
Does adding audio really make the model stronger? The answer is yes! The team found that sound provides a new information dimension for vision, and audio – video joint learning can significantly improve video understanding capabilities. The results (as shown in the following table) show that with each additional step, from using vision alone (Visual Alone) to vision + audio (Implicit Learning, IL) and then to vision + audio + omni – modal data engine (Explicit Learning, EL), performance soars. Especially after adding the data engine’s “explicit learning,” the model’s performance has made a huge leap on multiple benchmarks.
[Key Insight 3] Clash of the Titans: When OmniVinci Meets “Reinforcement Learning”
Can the base model, which is already so strong, evolve further? Yes, it can! Through reinforcement learning (RL)! Audio makes reinforcement learning even more powerful! When using the GRPO reinforcement learning framework, the team discovered a “hidden buff”: training the AI by just showing it videos (vision) is far less effective than training it while “watching and listening” (vision + audio combination). As shown in the figure, after adding audio, the model converges faster.
In this multi – modal RL framework, both OmniVinci and Qwen2.5 – Omni can benefit. However, with its stronger base performance and instruction – following ability, OmniVinci surpasses the accuracy rate of Qwen2.5 – Omni within 15 steps and converges 2.7 times faster in terms of format rewards. Finally, after RL training, OmniVinci + RL achieves an overall improvement across all omni – modal benchmarks.
Not Just SOTA, but an All – Round Agent
Benchmark scores are just the foundation. A true omni – modal AI must be able to show its skills in the real world. OmniVinci has done just that. The research team tested it in multiple real – world scenarios with excellent results:
Scenario 1: Joint Audio – Visual Perception
Give it a podcast video, and it can not only understand the appearance of the host and guests but also “understand” the complex topics they are discussing.
Scenario 2: Speech Transcription + Translation
When you speak to it, it can instantly transcribe it into text.

Scenario 3: Full – Voice Interaction
You ask with your voice, “What is the mission of this speaker’s company?” It immediately responds with its voice, “His company’s mission is to establish a self – sustaining civilization on Mars.”
Scenario 4: Commanding Robots by Just Speaking
OmniVinci can directly understand your voice commands (such as “Enter the bedroom and stand at the foot of the bed”) and then plan the next actions. This is truly practical human – machine interaction!
Scenario 5: AI Understands “Expert Consultations”
A doctor scrolls through CT images while verbally giving a diagnosis (“Here we see some pulmonary bullae and related fibrotic changes…”). OmniVinci can simultaneously “watch” the dynamic changes in the CT images and “understand” the doctor’s professional explanations, accurately answering difficult questions like “How have the lung textures changed over time?” and making a big splash in medical AI.
Scenario 6: AI “All – Round Commentary” for Sports Games
When watching a tennis match, AI is no longer “blind.” OmniVinci can simultaneously understand intense visual actions (who is serving, who wins the point) and the commentator’s comments. It outperforms Qwen2.5 – Omni in predicting score results and the length of rallies. More importantly, when quantified, it has extremely low latency on the consumer – grade graphics card GeForce RTX 4090 and can be fully used for TV broadcasts.
Is This Jarvis?
The emergence of OmniVinci may not just mark the birth of a new state – of – the – art (SOTA) 9B omni – modal model; it represents a brand – new AI paradigm. In the future, AI will no longer be fragmented “visual models” or “audio models” but unified “omni – modal perception systems.” Lower training costs mean faster iteration and wider application. From robots that can understand instructions to medical AI that can understand doctors’ oral descriptions and CT images, and to smart factories that can monitor abnormal sounds and images, a more intelligent future is accelerating its arrival.





